article written by Isabelle Chéry
Incubation is the accompaniment, by an organisation, of holders of a business creation project with innovation potential. This support consists of offering a set of services to secure the creation of a business. Incubation provides guidance to entrepreneurs in terms of strategic choices, financing, entrepreneurial training, accommodation and contact with an established network, etc. in the early stages of the start-up’s life (see S for Start-up). A “coach” provides support to the holders for personalised advice. The business incubator is the place where these innovative entrepreneurial projects are hosted.
There are several types of incubators. They differ in the services they offer, whether they are profit-making or not, and the type of projects they target. In particular, there are:
- Public incubators whose mission is to encourage the emergence and implementation of innovative business creation projects that make the most of the skills and results of the laboratories in public research and higher education institutions. They can host projects from public research laboratories and/or innovative projects from the economic world. These incubators can offer premises, support and funding for external services such as market research. These incubators generally operate on the principle of a repayable advance in the event of success.
- In Grenoble, the public incubator is the SATT Linksium, whose incubation process is described below.
- Internal incubators in schools or institutes that support students' entrepreneurial projects. These incubators can offer premises, resources (Internet access, telephony, reprography, etc.), support, training, and privileged access to the school's teachers and researchers. They offer networking with experienced entrepreneurs or with private or public players in business financing. This networking facilitates access to aid (loans of honour, other incubators, business incubators, etc.), which are considered to be selective, as well as contact with investors to organise an early fundraising round.
- In Grenoble, we have the Pôle Etudiants pour l’Innovation, le Transfert et l'Entrepreneuriat known as Pépite oZer.
- “Corporate” incubators developed by large industrial groups or service providers. Industrial groups’ objective is to encourage the emergence of start-ups that will enable the group’s activities to be adapted to the new economy specificities, to use new technologies, scientific discoveries or other, to promote the development of their activities, or to diversify into related activities.
- Private incubators, which often offer support to already financed young companies. Private incubators are profit-driven. They generally take a percentage of the supported company’s capital in order to earn a capital gain when the company is sold to a buyer, or when it is floated on the stock market.
- European incubators from European KIC consortia (Knowledge and Innovation Communities), academic/industrial alliances, which offer support for start-ups, from creation to development, with equity investments in specialised innovation sectors.
- Grenoble is home to the KIC InnoEnergy, of which Grenoble INP is a shareholder. KIC InnoEnergy incubates high-potential start-ups developing new technologies in the energy sector.
ZOOM ON INCUBATION AT SATT Linksium
SATT Linksium (see S comme SATT and L for Linksium) is Grenoble INP's preferred channel for the maturation and incubation of research results from laboratories. We present here the incubation process.I- CONDITIONS OF ENTRY TO THE INCUBATION
SATT Linksium finances the incubation process. It favours the creation of start-ups as a means of development for:
- A wide dissemination of the technologies stemming from the laboratories,
- A sustainable and significant financial return for the system,
- A significant economic impact on territories.
To enter the SATT Linksium incubation programme, the company must not have yet been created. The entry into incubation takes place when the technology has a sufficient maturity level. According to the Nasa TRL scale (see T for TRL), incubation starts for technologies located around TRL 6. Incubation lasts from 12 to 24 months.
There are two ways of entering incubation depending on the origin of the project. It may be the result of:
- (Case 1) A maturation project (see M for Maturation) initiated by a SATT Linksium shareholder institution;
- (Case 2) From an external sponsor.
In the case of an external promoter, in addition to the assets brought by this promoter, the State imposes a technical development link with SATT Linksium research laboratory shareholder in order to obtain transferable results from the laboratory to the future start-up. This condition is necessary to finance the support of a start-up project. The collaboration between the project leader and the laboratory is called "Maturation Technologique Flash (MTF)".
In both cases, once the company is created, a sub-licence on the Intellectual Property resulting from the maturation or MTF is set up between the SATT and the start-up (see A for Framework Agreement).
II- VARIOUS POSSIBLE SUPPORTS
Incubation offers support for the creation project in six areas:
1- Technology. The objective is to provide funding to complete the design of the future start-up's offer and to support the production of pre-series (funding of up to 30 k€).
2- Market actions. SATT Linksium assists start-ups in building and validating the “business mode”l. The business model describes the general operating logic of the start-up's project, i.e., its strategy for making money. It explains how the company creates, delivers and captures value. To formalise the business model, a simple tool to implement is the business model canvas (a tool taken from the book “Business model generation” by Alexander OSTERWALDER and Yves PIGNEUR, see Figure 1), which is a thinking tool for mapping the key elements of the project and organising them into a coherent, relevant and even innovative whole. The business model is a work of reflection, diagnosis and synthesis.
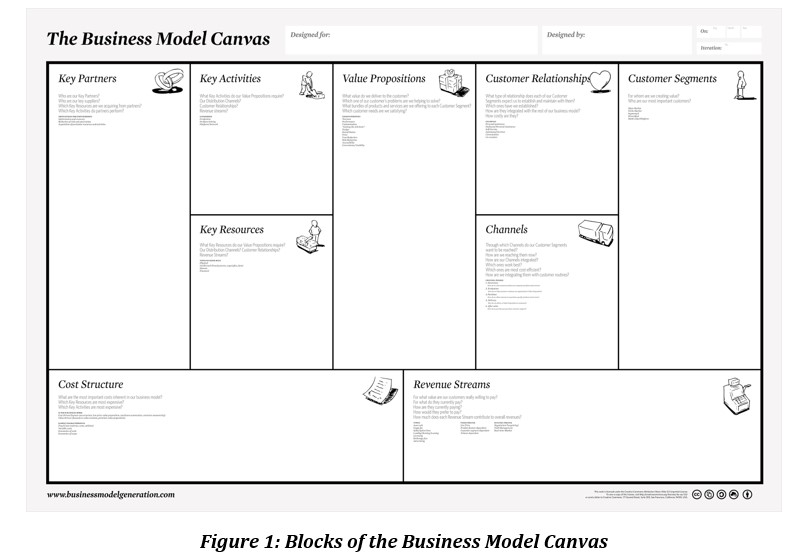
Next, the business plan (BP) must be drawn up. It explains the operational implementation (company strategy, manager's vision, etc.) and figures (projected balance sheet, projected income statement) of the economic model. The business plan is a formal presentation document of about thirty pages. In order to set up the BP, the promoter can obtain financing for a market study (analysis of companies in the sector, market segmentation, trends evolution, etc.).
The BP is a good tool for sharing and sharpening the project coherence for the entrepreneur and the stakeholders: it helps to clarify the objectives and the strategy. It is an alibi for team building: collective learning about each other, progressive adjustments or separation of co-founders. It is a communication tool for banks, investors, partners... It is a tool for continuous management and refocusing of actions: it is a dynamic guide.
3- Action Management. SATT Linksium helps project leaders build a solid team by putting them in touch with their future partners and by planning their recruitment. In order to function properly, it is crucial that the future company can count on a solid base of complementary skills from the partners. This base is made up of three pillars: the “company management” pillar, the “scientific and technical” pillar and the “business marketing” pillar. One person is not capable of assuming all these functions. At least two people must embody these core competencies. Investors will only commit if they are faced with a solid team. To this end, SATT Linksium has developed the Share K platform to bring together people interested in creating a company and to form this skills triad.
4- Legal action. The objective is to set up the valorisation strategy as well as the key contracts with partners. Contract models are drawn up with external consultancy firms. The legal aspects can also concern securing intellectual property through freedom of exploitation studies or prior art searches.
5- Communication action. SATT Linksium helps the project leaders access the of the future start-up's clients and partners with an adapted communication strategy.
6- Finance Action. The objective is to structure the financial aspects of the BP in order to mobilise the appropriate funding and attract investors. SATT Linksium puts entrepreneurs in touch with investors to help them raise funds.
Transversally, the applicant also has access to training on entrepreneurship. SATT Linksium prepares project leaders for the I-Lab competition, which is the national competition for the creation of innovative technology companies. For example, the SATT organises workshops between entrepreneurs in order to position themselves for the competition. The SATT coach advises entrepreneurs, for example on the minimum capital investment in order to have a leverage effect of 1 to 3 on financing from private banks or from innovation financing players such as the ADEME, etc.




